In the world of cryptocurrency, a blockchain wallet plays a crucial role in securing and managing digital assets. A wallet, in simple terms, is a digital address that allows users to send, receive, and store their cryptocurrencies. This comprehensive guide will provide you with a detailed understanding of what a blockchain wallet address is and how it functions within the distributed ledger system of blockchain technology.
At its core, a blockchain wallet address is a unique identifier that represents a user’s ownership of a certain amount of cryptocurrency. Just like a bank account number or an email address, a wallet address is used to facilitate transactions and verify ownership. Unlike traditional banking systems, however, a blockchain wallet operates within a decentralized network, ensuring that transactions are secure, transparent, and tamper-proof.
When a user creates a blockchain wallet, they are essentially generating a pair of cryptographic keys – a public key and a private key. The public key serves as the wallet address, enabling other users to send funds to the wallet. The private key, on the other hand, is kept secret and is used to access and manage the funds stored in the wallet. It is important to keep the private key secure, as anyone with access to it can control the funds within the wallet.
Every transaction made with a blockchain wallet is recorded on a distributed ledger called the blockchain. This ledger is distributed across a network of computers, known as nodes, and is constantly updated as new transactions occur. Each transaction is grouped together in a block, which is then added to the blockchain in a chronological order. This ensures that the entire history of transactions is readily available for anyone to verify, promoting transparency and eliminating the need for intermediaries.
In conclusion, a blockchain wallet address is a digital identifier that enables users to send, receive, and store cryptocurrencies within a distributed ledger system. Understanding the basics of how a blockchain wallet works is essential for anyone looking to engage with the world of cryptocurrency. By securely managing your wallet address and private key, you can ensure the safety of your digital assets and participate in the decentralized revolution that blockchain technology has to offer.
- What is a Cryptocurrency Wallet Address?
- How Does a Digital Wallet Address Work?
- The Significance of a Distributed Ledger Wallet Address
- The Anatomy of a Cryptocurrency Wallet Address
- Wallet and Address
- Blockchain and Distributed Ledger
- The Structure of a Wallet Address
- Checking the Validity of a Wallet Address
- Conclusion
- Types of Cryptocurrency Wallet Addresses
- 1. Public Addresses
- 2. Private Keys
- 3. Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) Wallets
- 4. Multisignature Addresses
- 5. Segregated Witness (SegWit) Addresses
- 6. Stealth Addresses
- 7. Vanity Addresses
- 8. Paper Wallets
- 9. Hardware Wallets
- 10. Exchange Wallets
- How to Generate a Digital Wallet Address
- The Importance of Securing Your Wallet Address
- 1. Protecting Your Digital Assets
- 2. Maintaining Data Privacy
- 3. Preventing Unauthorized Transactions
- 4. Protecting Against Loss
- 5. Safeguarding Against Phishing Attacks
- Final Thoughts
- Transactions and the Role of Wallet Addresses
- Frequently asked questions:
- What is a blockchain wallet address?
- How does a blockchain wallet address work?
- Are blockchain wallet addresses permanent?
- Can I have multiple wallet addresses?
- Are blockchain wallet addresses case-sensitive?
- Can I send different cryptocurrencies to the same blockchain wallet address?
- Videos:
- Crypto Wallets Explained! (Beginners’ Guide!) (2023 Edition!) ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Ultimate Step-by-Step!
- Blockchain Technology Explained (2 Hour Course)
- Bitcoin 101: The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Crypto
What is a Cryptocurrency Wallet Address?
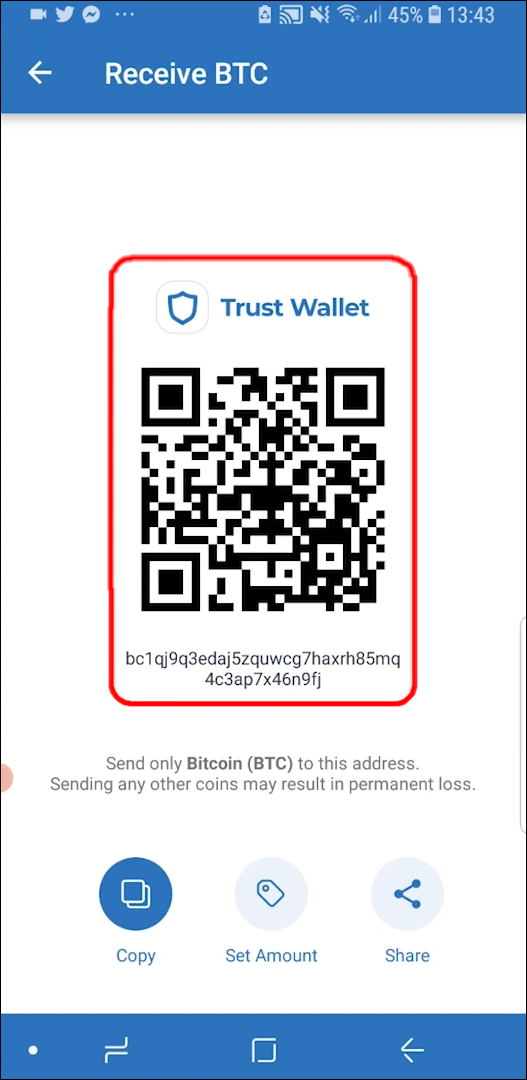
A cryptocurrency wallet address is a unique identifier used to receive, store, and send cryptocurrencies. It serves as the location where your digital assets are stored on the blockchain. In simple terms, it can be compared to a bank account number, where you can receive funds and make transactions.
Blockchain, the technology behind cryptocurrencies, is a distributed ledger that records and verifies transactions. This ledger is maintained by a network of computers, known as nodes, which work together to validate and authenticate transactions. Each transaction is grouped together in a block and added to the blockchain in a chronological and immutable manner.
A cryptocurrency wallet address is a representation of your ownership of a specific amount of a particular cryptocurrency. It consists of a combination of alphanumeric characters, usually in the form of a long string or a QR code. Wallet addresses are generated using cryptographic techniques to ensure their uniqueness and security.
It is important to note that each cryptocurrency has its own unique wallet address format. For example, Bitcoin wallet addresses start with a “1” or “3,” while Ethereum wallet addresses start with “0x” followed by a string of letters and numbers. Using an incorrect wallet address format can result in the loss of funds, so it is crucial to double-check before making any transactions.
A cryptocurrency wallet is a software application that allows users to interact with the blockchain and manage their digital assets. It stores the private keys, which are required to access and control the funds associated with a wallet address. Wallets can be categorized into various types, including hardware wallets, software wallets, online wallets, and paper wallets. Each type has its own security features and convenience factors.
When someone wants to send you cryptocurrency, they can do so by entering your wallet address as the destination for the transaction. Once the transaction is initiated, it is broadcasted to the network, where it awaits confirmation. Miners, who are responsible for validating and adding transactions to the blockchain, will include the transaction in the next block. Once confirmed, the cryptocurrency will be transferred to your wallet address, making it available for your use or further transactions.
In summary, a cryptocurrency wallet address is a fundamental component of the blockchain ecosystem. It enables users to receive, store, and send cryptocurrencies securely and efficiently. By understanding the basics of wallet addresses and utilizing proper security measures, individuals can better safeguard their digital assets in this ever-evolving digital age.
How Does a Digital Wallet Address Work?
A digital wallet address is a unique identifier in the cryptocurrency world that allows users to send and receive digital currencies. It is an essential element in blockchain technology, which is the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
When a user creates a digital wallet, they are assigned a unique wallet address. This address acts as their public key in the cryptocurrency network, allowing other users to send them funds.
The digital wallet address is based on cryptographic algorithms and is typically a long string of alphanumeric characters. This address is generated by the wallet software and is associated with the user’s private key, which is used to authenticate and authorize transactions.
When a user wants to receive cryptocurrency, they provide their wallet address to the sender. The sender then includes the recipient’s wallet address in the transaction details, indicating that the funds should be transferred to that specific address.
Behind the scenes, the blockchain network maintains a ledger of all transactions. The ledger is a distributed database that records every transaction ever made in the network. When a transaction is initiated, it is broadcasted to the network and verified by multiple nodes (computers) in the network.
Once a transaction is verified and added to a block, it becomes a permanent part of the blockchain. The recipient’s wallet address is updated with the new transaction, reflecting the received funds in their wallet.
It is important to note that a digital wallet address does not actually hold the cryptocurrency. Instead, it provides a secure way to identify and access the funds associated with that address in the blockchain ledger.
Having a unique digital wallet address for each transaction ensures that transactions can be easily tracked and verified. Additionally, it adds an extra layer of security as the wallet address alone does not provide access to the funds; the private key is required to authorize transactions and access the funds.
In summary, a digital wallet address is a unique identifier that allows users to send and receive cryptocurrency. It is generated by the wallet software and is associated with the user’s private key. The address is used to identify and access the funds in the blockchain ledger, and transactions involving the address are recorded on the distributed ledger.
The Significance of a Distributed Ledger Wallet Address
In the world of blockchain and cryptocurrency, a wallet address plays a crucial role in facilitating transactions and securing digital assets. It is an alphanumeric string that serves as a unique identifier for a cryptocurrency holder. When it comes to distributed ledger technology, the wallet address becomes even more significant.
A distributed ledger, such as the blockchain, is a decentralized database that stores transactional records across multiple computers or nodes. It ensures transparency, security, and immutability by utilizing cryptographic techniques. Each node in the network holds a copy of the entire blockchain, which includes all the transactional data.
A wallet address is essential in this distributed ledger system as it allows users to send and receive cryptocurrency securely. It is generated through a process using cryptographic algorithms, ensuring the uniqueness and security of the address. The wallet address is usually represented as a combination of letters and numbers, making it virtually impossible to guess or forge.
When a user wants to send cryptocurrency to another person, they need to specify the recipient’s wallet address. This allows the transaction to be recorded on the blockchain and verified by the network nodes. The wallet address acts as a destination for the funds and ensures that the transaction is properly recorded and accounted for.
Additionally, wallet addresses provide users with a level of anonymity. While transactions recorded on the blockchain are transparent and visible to everyone, the wallet addresses are not directly linked to personal identification information. This pseudonymity provides users with privacy and protects their identities while engaging in cryptocurrency transactions.
The significance of a distributed ledger wallet address goes beyond just facilitating transactions. It is a fundamental component of the decentralized nature of blockchain and cryptocurrency. By using unique wallet addresses, users can securely store and manage their digital assets without relying on a centralized authority. This decentralization ensures that no single entity has control over the transactions or can manipulate the ledger for their benefit.
In conclusion, the distributed ledger wallet address serves as a vital element in the world of blockchain and cryptocurrency. It provides security, privacy, and allows for the transparent recording of transactions. With its unique alphanumeric structure, it ensures the integrity of the decentralized system and empowers users to have full control over their digital assets.
The Anatomy of a Cryptocurrency Wallet Address
A cryptocurrency wallet address is a fundamental component of the distributed ledger technology known as blockchain. It serves as a unique identifier for a wallet within the blockchain network. Understanding the structure and composition of a cryptocurrency wallet address is crucial for securely transacting and storing digital currencies.
Wallet and Address
A cryptocurrency wallet is a digital wallet that allows users to store, manage, and transact with their digital assets. It consists of a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is used to generate a wallet address, while the private key is used to sign transactions made from that address.
A wallet address, also known as a public address, is a cryptographic hash of the wallet’s public key. It is a string of alphanumeric characters that uniquely identifies the wallet within the blockchain network.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger
A blockchain is a distributed ledger that records all transactions made within a cryptocurrency network. It consists of a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of verified transactions. The blockchain is distributed across multiple computers, known as nodes, making it decentralized and resistant to tampering.
The Structure of a Wallet Address
A cryptocurrency wallet address typically consists of alphanumeric characters, represented in a base58 or base64 encoding format. The exact structure and length of a wallet address vary depending on the cryptocurrency.
For example, Bitcoin wallet addresses start with a 1 or 3 and are 26-35 characters long, while Ethereum wallet addresses start with 0x and are 42 characters long.
It is important to note that a wallet address is case-sensitive, so even a minor change in capitalization can result in an invalid address.
Checking the Validity of a Wallet Address
Due to the sensitive nature of cryptocurrency transactions, it is crucial to verify the validity of a wallet address before sending any funds. Most cryptocurrency wallets and exchanges provide address validation mechanisms to ensure that the entered address is correct.
Additionally, users can use online tools or libraries to perform checksum verifications or even manually verify the checksum themselves.
Conclusion

A cryptocurrency wallet address is a vital component in the world of digital currencies. It serves as a unique identifier for a wallet within a blockchain network and is crucial for securely transacting and storing cryptocurrencies. Understanding the structure and validating the integrity of a wallet address is essential for ensuring the safety and accuracy of cryptocurrency transactions.
Types of Cryptocurrency Wallet Addresses
A cryptocurrency wallet address is a unique identifier that is used to send and receive cryptocurrency on a blockchain network. There are several types of cryptocurrency wallet addresses, each with its own features and use cases.
1. Public Addresses

Public addresses, also known as receiving addresses, are used to receive cryptocurrency. They are generated by the wallet software and are publicly visible on the blockchain. Public addresses are often represented as a long string of alphanumeric characters and can be shared with others to receive funds.
2. Private Keys
A private key is a randomly generated string of characters that is used to authorize transactions and access the funds stored in a cryptocurrency wallet. Private keys should be kept secret and secure, as anyone who has access to the private key can control the associated funds.
3. Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) Wallets
HD wallets are designed to generate a sequence of public addresses from a single master seed. This seed is generated by the wallet software and can be used to restore all the addresses and private keys in the wallet. HD wallets offer enhanced security and convenience by allowing users to backup and restore their wallets easily.
4. Multisignature Addresses
A multisignature address, also known as a multi-sig address, requires multiple signatures to authorize a transaction. This type of address is often used in business or group settings, where multiple parties need to approve transactions. Multisignature addresses provide an extra layer of security and reduce the risk of unauthorized access to funds.
5. Segregated Witness (SegWit) Addresses
SegWit addresses are a type of bitcoin address that offers several benefits, including faster transaction confirmations and lower fees. SegWit addresses are backward-compatible with older bitcoin addresses, but they can support additional features such as the Lightning Network.
6. Stealth Addresses
Stealth addresses are designed to provide privacy and anonymity in cryptocurrency transactions. When a user wants to receive funds, a unique stealth address is generated by the wallet software. This address is linked to the recipient’s public key, but it cannot be publicly associated with the recipient’s identity.
7. Vanity Addresses
Vanity addresses are custom addresses that are specifically generated to include personalized or recognizable words or patterns. Although vanity addresses do not offer any additional security or functionality, they can be used for branding purposes or as a personal touch.
8. Paper Wallets
A paper wallet is a physical printout or handwritten document that contains the public and private keys of a cryptocurrency wallet. Paper wallets are offline and offer enhanced security against online threats. However, they can be vulnerable to physical damage or loss, so proper precautions should be taken to protect and backup the paper wallet.
9. Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets are physical devices that securely store cryptocurrency and private keys. They are designed to provide enhanced security by keeping the private keys offline and separate from potentially compromised computer systems. Hardware wallets are considered one of the most secure options for storing cryptocurrency.
10. Exchange Wallets
Exchange wallets are provided by cryptocurrency exchanges and are used to store and manage cryptocurrency assets on the exchange platform. While exchange wallets offer convenience for trading and exchanging cryptocurrency, they come with the risk of potential security breaches and loss of funds if the exchange is hacked.
In conclusion, there are various types of cryptocurrency wallet addresses, each with its own characteristics and purposes. It is essential to choose the appropriate wallet address based on factors such as security, convenience, and specific use cases.
How to Generate a Digital Wallet Address
A digital wallet address is a unique identifier used to receive or send cryptocurrency. It is generated using the blockchain technology, which is a distributed ledger that records all cryptocurrency transactions.
Generating a digital wallet address is simple and can be done in a few steps:
- Choose a wallet provider: There are several wallet providers available in the market. Choose a trusted and reliable provider that supports the cryptocurrency you want to use.
- Sign up for an account: Create an account with the wallet provider by providing your personal information and following the registration process.
- Create a new wallet: Once you have signed up, you can create a new wallet. The wallet provider will guide you through the process and generate a unique wallet address for you.
- Secure your wallet: It is important to secure your wallet by enabling two-factor authentication, setting a strong password, and keeping your private keys safe.
- Receive or send cryptocurrency: With your newly generated wallet address, you can now receive cryptocurrency from others or send cryptocurrency to others by entering their wallet address.
It is important to note that each cryptocurrency has its own unique address format. Make sure to use the correct address format when receiving or sending cryptocurrency. Using the wrong address format may result in the loss of your funds.
Always double-check the wallet address before making any transactions to ensure that you are sending or receiving cryptocurrency to the correct address. Once a transaction is made, it cannot be reversed.
To summarize, generating a digital wallet address involves choosing a wallet provider, creating an account, creating a new wallet, securing your wallet, and using the generated address to receive or send cryptocurrency. Make sure to follow proper security practices to protect your funds.
The Importance of Securing Your Wallet Address
When it comes to cryptocurrency, securing your wallet address is of utmost importance. Your wallet address is the digital equivalent of your bank account number in the traditional financial system. Just like you would protect your bank account details, it is crucial to take necessary precautions to safeguard your cryptocurrency wallet address.
1. Protecting Your Digital Assets
Your wallet address is used to store and manage your digital assets, such as Bitcoin or any other cryptocurrency. If someone gains access to your wallet address, they can potentially steal your funds. By securing your wallet address, you reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect your digital wealth.
2. Maintaining Data Privacy
The blockchain, a distributed ledger technology, ensures the transparency and security of transactions. However, the wallet addresses used in these transactions are usually pseudonymous, meaning they do not directly reveal the identities of the users. Securing your wallet address helps maintain your privacy and prevents potential malicious actors from linking your address to your real-world identity.
3. Preventing Unauthorized Transactions
If someone gains access to your wallet address, they could potentially initiate transactions without your consent. By implementing security measures, such as using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly updating your software, you significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized transactions.
4. Protecting Against Loss

If you lose access to your wallet address, whether due to a hacking incident, hardware failure, or human error, you could lose your funds permanently. By securing your wallet address with backup solutions, such as mnemonic phrases or paper wallets, you mitigate the risk of losing access to your cryptocurrencies.
5. Safeguarding Against Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are common in the cryptocurrency space, where malicious individuals attempt to trick users into revealing their wallet addresses and private keys. By being cautious and following best practices, such as not clicking on suspicious links or sharing your sensitive information, you can protect yourself against phishing attempts and keep your wallet address secure.
Final Thoughts
In summary, securing your wallet address is crucial to safeguard your cryptocurrency funds, maintain data privacy, prevent unauthorized transactions, protect against loss, and safeguard against phishing attacks. Implementing robust security measures, being vigilant, and staying updated on the latest security practices will help ensure the safety of your digital assets.
Transactions and the Role of Wallet Addresses

In the world of blockchain and cryptocurrency, transactions play a crucial role in the transfer of digital assets. These transactions are recorded on a distributed ledger known as the blockchain. A wallet address is a key component in facilitating these transactions.
A blockchain is a distributed and decentralized digital ledger that records all transactions in a transparent and secure manner. It functions as a public database where transactions are stored in blocks, linked together in a chronological order.
A wallet address, also known as a public key, is a unique identifier used to receive or send cryptocurrencies. It is a combination of alphanumeric characters that represents a user’s ownership of a certain amount of cryptocurrency. Every address corresponds to a specific wallet, which is essentially a software application or a hardware device used to manage and store cryptocurrency.
When a user initiates a transaction, they specify the wallet address of the recipient and the amount of cryptocurrency they wish to transfer. The transaction is then verified and recorded on the blockchain network. This verification process involves validating the digital signatures associated with the wallet addresses involved in the transaction. Once the transaction is confirmed, the transferred cryptocurrency is deducted from the sender’s wallet address and added to the recipient’s wallet address on the blockchain ledger.
The wallet address plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of transactions. As the address is derived from a user’s private key, which should be kept confidential, it provides a layer of authentication and ownership verification. Furthermore, the use of wallet addresses allows for anonymity in transactions, as they do not reveal the personal information of the users involved.
It is important to note that wallet addresses are specific to each cryptocurrency. For example, a Bitcoin wallet address cannot be used to receive Ethereum or any other cryptocurrency. This ensures that transactions are accurately recorded on the respective blockchain ledgers and prevents any potential mix-ups.
In conclusion, wallet addresses are an essential component of cryptocurrency transactions. They serve as unique identifiers for users’ ownership of digital assets and play a vital role in the verification and recording of transactions on the blockchain ledger. Understanding how wallet addresses work is crucial for anyone looking to engage with cryptocurrencies and make secure transactions.
Frequently asked questions:
What is a blockchain wallet address?
A blockchain wallet address is a unique identifier that allows individuals to receive, store, and send cryptocurrencies on the blockchain network.
How does a blockchain wallet address work?
A blockchain wallet address is generated through a process called cryptographic hashing. This process converts a user’s private key into a shorter string of characters that serves as a public address for receiving funds. Transactions sent to this address are recorded on the blockchain and can be accessed by the user’s private key to prove ownership and authorize transfers.
Are blockchain wallet addresses permanent?
Blockchain wallet addresses are generally permanent, meaning they do not change unless the user specifically generates a new address. However, some advanced wallets may offer the option to create multiple addresses or to generate new addresses for increased privacy.
Can I have multiple wallet addresses?
Yes, many blockchain wallets allow users to have multiple addresses. This can be useful for organizing funds, maintaining privacy, or managing different types of cryptocurrencies.
Are blockchain wallet addresses case-sensitive?
Yes, blockchain wallet addresses are case-sensitive. It is important to enter the address exactly as it is provided to avoid any errors in sending or receiving funds.
Can I send different cryptocurrencies to the same blockchain wallet address?
No, blockchain wallet addresses are specific to particular cryptocurrencies. Each cryptocurrency has its own unique address format, and sending the wrong cryptocurrency to a wallet address could result in permanent loss of funds.
Videos:
Crypto Wallets Explained! (Beginners’ Guide!) (2023 Edition!) ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Ultimate Step-by-Step!
Blockchain Technology Explained (2 Hour Course)
Bitcoin 101: The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Crypto








