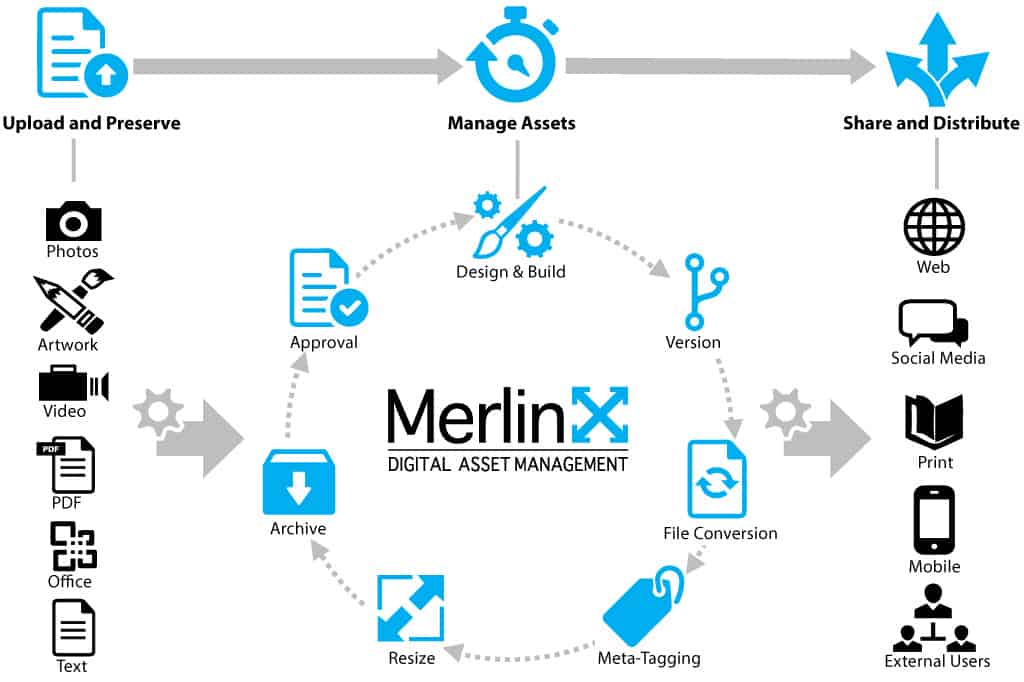
In today’s digitally-focused world, the concept of digital assets has become increasingly important. Digital assets can be defined as any form of information or content that is created, stored, or transmitted digitally. This includes everything from photographs and videos to documents and audio files.
Unlike physical assets, digital assets can be easily duplicated, shared, and treated as a commodity. In fact, the rise of digital assets has led to a new era of publishing, where anyone can create and share their work with the world. Whether it’s publishing a blog post, uploading a video to a social media platform, or sharing a song on a streaming service, digital assets have revolutionized the way we consume and interact with content.
One of the key advantages of digital assets is their ability to be stored and accessed from anywhere at any time. In the past, physical assets such as books or artwork could only be viewed or accessed in specific locations. With digital assets, you can access your favorite book or listen to your favorite song from your phone or computer, no matter where you are.
However, with the rise of digital assets comes a number of challenges and risks. For example, the digital nature of these assets makes them vulnerable to loss or damage. Whether it’s a computer crash, a cyber attack, or a simple mistake, losing access to your digital assets can be devastating. That’s where digital asset management comes in.
Digital asset management involves the process of organizing, storing, and protecting your digital assets. It can be as simple as creating a backup of your files or as complex as implementing a secure system for managing your company’s digital assets. By effectively managing your digital assets, you can ensure that they are protected, easily accessible, and ready to be shared or monetized.
So, whether you’re a photographer looking to showcase your portfolio, a musician wanting to share your latest album, or a business owner needing to store and protect important documents, digital assets play a vital role in today’s digital landscape.
- Definition of Digital Assets
- Additional Information
- Publications
- Related Topics
- IRS Guidance
- Tax Consequences
- Guidance and Publications
- Frequently Asked Questions:
- What are digital assets?
- How are digital assets stored?
- Why are digital assets important?
- What are the risks associated with digital assets?
- Video:
- Digital Assets 101: Transaction Basics | Fireblocks Academy
- WHY I’M BUYING LESS BITCOIN TODAY. XRP UPDATE.
- Effects of digital assets in the finance industry
Definition of Digital Assets
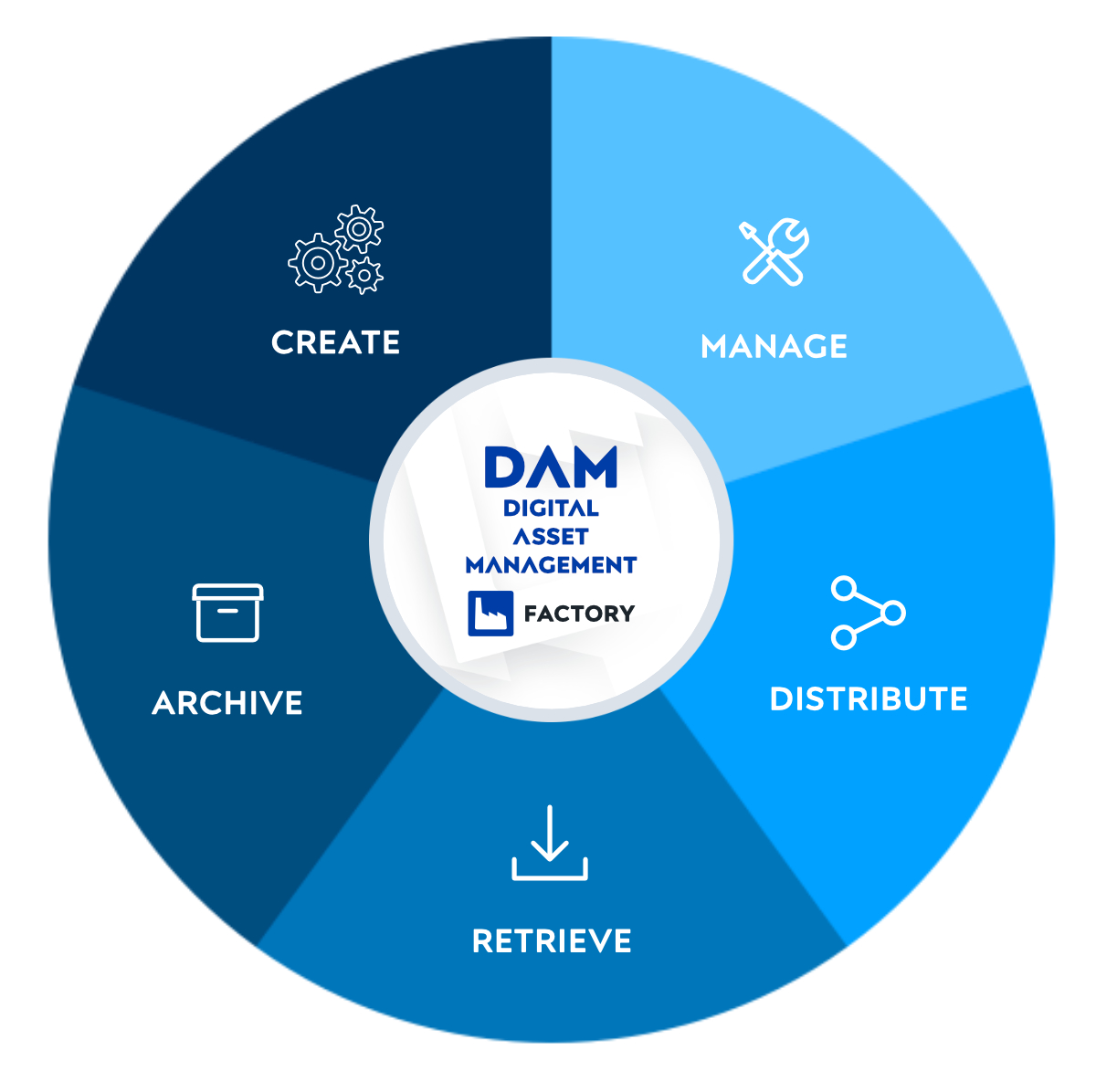
In the context of this publication, the term “Digital Assets” refers to your digitally stored or created materials that hold value or importance to you or your organization.
It is important to notice that digital assets can take various forms, such as:
- Text documents
- Images
- Audio files
- Video files
- Presentations
- Website content
- Computer code
- Data files
- And many others
These assets can be stored on your personal computer, mobile device, or in cloud storage platforms, and can range from personal files to business-related materials.
It is crucial to recognize that digital assets should be treated with the same attention and care as physical assets. Just like you would protect physical documents or valuables, your digital assets should also be protected to prevent loss, theft, or unauthorized access.
This publication describes the importance of safeguarding your digital assets and provides recommendations on how to protect and manage them effectively.
Additional Information

The following table provides additional information on digital assets:
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Bank Accounts | This category includes any digital records related to your bank accounts, such as statements, transaction records, and login information. |
|
| Publications | These are digital assets related to published works, including articles, books, or journals that you may have authored or contributed to. |
|
| Legal Documents | This category involves any legal documents that are stored digitally, such as contracts, wills, or power of attorney. |
|
| Personal Photos and Videos | These assets include any digital media files that capture personal moments, such as photos and videos from your personal life. |
|
| Notice of Death | This category involves any digital records related to the notification of your passing, such as death certificates or obituaries. |
|
It is important to note that these examples are not exhaustive, and the nature and value of digital assets can vary widely depending on individual circumstances. Furthermore, the way these assets are treated legally and financially also differs from traditional physical assets. It is therefore crucial to seek professional guidance and engage in proper estate planning to ensure the adequate management and distribution of your digital assets.
Publications
One of the main advantages of digital assets is the ability to create and distribute publications in a digital format. This allows for instant access to information on various devices and platforms.
Digital assets can include documents, such as reports, whitepapers, and articles, as well as multimedia content, such as videos and podcasts. These assets can be shared through various channels, including websites, social media platforms, and email newsletters.
When it comes to publications involving digital assets, it is important to consider copyright and intellectual property rights. Just like any other form of content, it is essential to respect the original creators and give proper credit when using their work.
One advantage of digital assets is that they can be easily updated and revised. If there are any changes or improvements to a publication, it can be modified digitally, and the updated version can be distributed without the need for physical printing or distribution.
Your digital assets, including publications, can be protected through various means, such as watermarks, encryption, and digital rights management (DRM) systems. These measures can help prevent unauthorized copying and ensure that your assets are used in accordance with your terms and conditions.
Notice that the way digital assets are treated and protected can vary depending on the platform or system they are hosted on. For example, a bank may have stricter security measures in place compared to a personal blog.
Overall, publications are an important component of digital assets. They allow for the dissemination of information, the sharing of knowledge, and the promotion of ideas. With the right strategies and protection measures, digital publications can play a significant role in reaching and engaging a wider audience.
Related Topics

- Publication: Learn more about the importance of digital assets management in our recent publication.
- Involving Your Bank: Discover how to involve your bank in the management of your digital assets.
- Treated Digitally: Find out how digital assets are treated differently compared to physical assets.
- Notice: Understand the importance of giving proper notice for the transfer or disposal of digital assets.
- Digital Assets: Explore the different types of digital assets and their significance.
For more information on these related topics, please refer to the respective sections in our publication. It is crucial to stay informed and updated on the management and protection of digital assets in today’s digital world.
IRS Guidance
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has provided guidance on how assets involving digital currency should be treated for tax purposes. The IRS Notice 2014-21 states that digital currency should be treated as property for federal tax purposes. This means that the general tax principles applicable to property transactions will also apply to transactions involving digital assets.
In the notice, the IRS explains that if you receive digital currency as payment for goods or services, it should be included in your gross income at the fair market value of the digital currency in U.S. dollars at the time of receipt. This means that if you receive digital currency as payment, you will need to determine the fair market value of the digital currency and report it as income.
The notice also states that if you mine digital currency, the fair market value of the virtual currency as of the date of receipt is includible in your gross income. This means that the value of the digital currency you mine will need to be reported as income.
If you sell or exchange digital currency, you may have a capital gain or loss. The notice explains that a capital gain or loss is the difference between the fair market value of the digital currency at the time of the sale or exchange and your adjusted basis in the digital currency.
The IRS publication 544 provides more detailed information on how to calculate capital gains and losses. It is important to keep track of your transactions involving digital assets and consult with a tax professional to ensure accurate reporting.
It is worth noting that the IRS’s guidance on digital assets is not limited to cryptocurrency, but also applies to other types of digital assets, such as digital tokens and virtual currencies.
| – Digital currency is treated as property for federal tax purposes. |
| – If you receive digital currency as payment, it should be included in your gross income at its fair market value. |
| – If you mine digital currency, its fair market value at the time of receipt is included in your gross income. |
| – Selling or exchanging digital currency can result in capital gains or losses. |
Tax Consequences

The tax consequences of digital assets can be both complex and significant. This section describes how digital assets are treated for tax purposes and the potential tax implications involved.
For tax purposes, digital assets are treated similarly to other assets such as money held in a bank account or stocks. This means that any gains or losses arising from the sale or exchange of digital assets may be subject to tax.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has provided some guidance on the tax treatment of digital assets in Publication 544. According to this publication, digital assets are considered property for federal tax purposes. Therefore, transactions involving digital assets must be reported on your tax return.
When it comes to taxes, there are generally two types of transactions involving digital assets: buying and selling, and using digital assets to purchase goods and services. In the first case, any gains made from selling digital assets may be subject to capital gains tax. On the other hand, if you use digital assets to buy goods or services, the value of the digital assets at the time of the transaction may be treated as income and subject to income tax.
It’s important to keep track of your transactions involving digital assets and properly report them on your tax return. Failure to do so could result in penalties and interest from the IRS. Additionally, if the IRS determines that you have not properly reported your transactions, you may be subject to an audit.
In conclusion, the tax consequences of digital assets can be complex, and it’s important to understand how they are treated for tax purposes. It’s recommended to consult with a tax professional who specializes in digital assets to ensure compliance with tax laws and to minimize any potential tax implications.
Guidance and Publications

When it comes to digital assets, it’s important to stay informed and up-to-date with the latest guidance and publications. Understanding how digital assets are treated and regulated can help you navigate the ever-changing digital landscape.
One valuable resource is the publication titled “Digital Assets: A Comprehensive Guide.” This publication provides a thorough overview of digital assets, their characteristics, and their importance in today’s digital age. It covers topics such as what digital assets are, how they are created and stored, and the various types of digital assets that exist.
Another important resource is the “Notice on Digital Assets” issued by your bank. This notice provides specific guidance on how your bank handles digital assets and what you need to be aware of when it comes to involving your bank in any digital asset transactions. It outlines the bank’s policies, procedures, and safeguards to protect your digital assets.
Furthermore, there are various online guidance and publications available from regulatory bodies and industry organizations. These resources offer insights into the regulatory environment surrounding digital assets and provide best practices for individuals and businesses alike.
It’s crucial to regularly review these guidance and publications to stay informed on the latest developments in the digital assets space. By doing so, you can make informed decisions about your digital assets and ensure their security and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are digital assets?
Digital assets are any form of content, information, or data that exists in digital form and has value. They can include photos, videos, music, documents, digital currencies, and more.
How are digital assets stored?
Digital assets can be stored in a variety of ways, including on personal computers, external hard drives, cloud storage services, and blockchain networks.
Why are digital assets important?
Digital assets are important for several reasons. Firstly, they enable the easy creation, storage, and sharing of content. Secondly, they can have significant monetary value, especially in the case of digital currencies. Lastly, they are essential for businesses and individuals to stay competitive and relevant in the digital age.
What are the risks associated with digital assets?
There are several risks associated with digital assets. One major risk is the potential loss or theft of digital assets, especially if proper security measures are not in place. Additionally, there is the risk of technological obsolescence, where digital assets may become inaccessible or unusable due to changes in technology. Lastly, there is the risk of legal and regulatory issues surrounding digital assets, which can vary depending on the jurisdiction.
Video:
Digital Assets 101: Transaction Basics | Fireblocks Academy
WHY I’M BUYING LESS BITCOIN TODAY. XRP UPDATE.
Effects of digital assets in the finance industry